Sizing SAP Solutions - Business Oriented, Proven, Cost EffectiveSizing means determining the hardware requirements of an SAP System such as network bandwidth, physical memory, CPU power, and I/O capacity. This presentation held at WIS conference in Amsterdam 2017 describes the sizing process for SAP S/4HANA. It describes when to use the HANA Quick Sizer and when to use the sizing reports. Hardware Certification Co-Innovated with SAP Spotlights. Sizing SAP S/4HANA using the Quick Sizer Tool. End-To-End Sizing Calculation – Gateway Customer. With sizing calculation process in order to find. To add more hardware for your existing SAP. If there is already a project entered in to SAP's Quick Sizer tool then those numbers. The aim of this sizing form is to provide a structure for entry of the information required to size the required hardware for an SAP project. The form is based off SAP's Quick Sizer, as are most of the help texts - the text of these are. Dell SAP sizing.
It is vital to size your SAP HANA hardware correctly to realize the maximum benefit from your investment and reduce your long-term total cost of ownership. Inadequate and over-provisioned sizing of SAP HANA could lead excess capacity and bloated hardware while under-provisioning can cause unexpected delays which will increase the cost of operational performance.

For the most part, sizing of SAP HANA database is based on the main memory which is determined by the amount of the actual data stored in memory. Since the data is compressed in HANA and the compression results depends on the used scenario, it is not easy to guess the amount of memory needed for sure. Therefore, the memory sizing for SAP HANA should be performed using SAP Quick Sizer tool, relevant SAP notes and SAP sizing reports.
Depending on the SAP HANA deployment, sizing approach would be different.
SAP Quick Sizer
For SAP HANA greenfield implementations, it is necessary to size the memory using the SAP Quick Sizer tool. The Quick Sizer calculates CPU, disk, memory and I/O resources based on the throughput numbers and can help you translate business requirements into technical requirements. For greenfield sizing, complete the following steps:
- Access the Quick Sizer tool (SAP HANA version)
- Create a sizing project – input your customer scenario data into Quick Sizer and it will display the results.
- Check for sample configurations and find the appropriate hardware configurations on SAP Standard Application Benchmark: http://www.sap.com/solution/benchmark.html
- Provide the project name to your hardware vendor and they will be able to propose an appropriate hardware configuration.
- If you are unable to find the right sizing for your SAP product in the Quick Sizer tool, consult the sizing guidelines and SAP notes (details below)
Simply fill the online questionnaire based on business-oriented figures and the results you obtain can help you select an economically balanced system that matches your company’s business goals. This is especially useful for initial budget planning.
Sizing BW on HANA
For systems that are migrated to SAP HANA, if the migration is from an SAP NetWeaver based system, use the sizing reports provided by SAP:
For BW on HANA migrations, use the following SAP notes:
- SAP Note 1637145 – SAP BW on HANA: Sizing SAP In-Memory Database
- SAP Note 1736976 – Sizing Report for BW on HANA
These two SAP notes explain the sizing approach of SAP BW system on SAP HANA including the sizing report and guidelines. The sizing here includes the memory sizing (column, row store and additional components) and disk sizing for data and log files. Note that the report could run up to 8-12 hrs depending on your system so it would be better to run it on a non-Production system first.
Below figure shows an example sizing report result for SAP BW on SAP HANA memory:
Sizing Suite on HANA, S/4HANA
For Suite on HANA migrations, use the following SAP notes:
- SAP Note 1793345 – Sizing for SAP Suite on HANA
- SAP Note 1872170 – Business Suite on HANA and S/4HANA sizing report
These two SAP notes describe the approach for Business Suite system on SAP HANA and SAP S/4 HANA. There is also a sizing script and guideline attached to these notes. See below for an example sizing report for Suite on SAP HANA memory:
After getting the memory sizing results via sizing reports described in the above SAP notes, check SAP HANA Hardware directory for hardware that matches your memory sizing results. For now, you don’t need to worry about storage and CPU sizing as they are already included in the certified SAP HANA appliances.
Sizing SAP HANA for non-NetWeaver approach
If the migration is from a non-SAP NetWeaver data source, you can use the approach described in SAP Note 1514966 – SAP HANA 1.0: Sizing SAP In-Memory Database. This SAP note explains the sizing of SAP HANA in a non-NetWeaver scenario, for instance, if the data is coming from an external source for SAP HANA to process and analyse. These sizing rules should not be used for sizing SAP BW or SAP Suite on HANA or SAP S/4HANA sizing.
General sizing approach for SAP HANA (for the non-NetWeaver approach) is basically determining static and dynamic memory requirements. The static memory requirement is related to the amount of main memory that is used for holding the table data which is the amount of disk space covered by the corresponding database tables (indexes not included). It is required to calculate the uncompressed data volume that is to be loaded into HANA using the tools attached to SAP Note 1514966 and apply the compression factor from the attachments to the sizing notes.
Additional memory is required also for objects that are created dynamically when new data is created or queries executed. Simply multiply static memory requirement by two as it is recommended by SAP to size dynamic memory same as static memory.
Sizing SAP HANA for Tailored Data Center Integration (TDI)
If you are planning to build SAP HANA system based on SAP HANA TDI (Tailored Data Center Integration) approach by using the available hardware or to reuse existing hardware to reduce hardware cost, you must become TDI certified and meet SAP HANA storage requirements. TDI follows the approach of SAP sizing and mapping to authorized servers, network and storage.
Sizing SAP HANA TDI consists of three main steps:
- Memory sizing for static and dynamic data
- Disk sizing for persistence storage
- CPU sizing for transactions, queries and calculations
As the first step to sizing SAP HANA TDI system, you should perform a memory sizing. Depending on the use case, you can use SAP Quick Sizer and/or above SAP notes for sizing Suite/BW on HANA. IBM also provides a process to support mapping of the SAP sizing to a hardware configuration that would meet your sizing demands. For more information, see SAP Note 2055470 and 2188482.
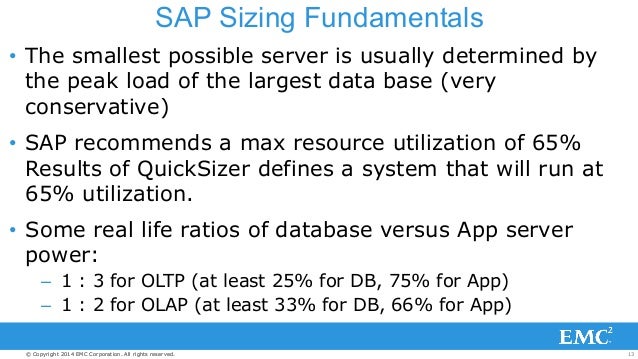
See below for more details about Disk and CPU sizing.
Disk Sizing
Persistent storage distinguishes between the data volume and log volume. In the data volume, basically a copy of the in-memory data persists and changed data is written to the data volume. The log volume is required to ensure the recovery of the database with zero data loss in case of a failure, so each transaction in SAP HANA is recorded as a redo log entry.
The recommended size of a data volume is equal to the calculated results from the sizing reports. Use value “Net data size on disk” and an additional free space of 20%. The figure shows an example sizing report result:
As you can see the sizing report, net data size on disk is calculated around 1.3TB. In this case, our minimum requirement for “data” volume would be around 1.6TB, considering the additional 20% free space.
During the migration of non-HANA DB to SAP HANA, the system may require a little more space than the actual calculated net data size on disk, but with enterprise storage, that is not considered relevant for the overall storage sizing
The minimum size of log volume depends on the number of data changes occurring between two SAP HANA savepoints which is by default created every five minutes. More data changes happening during this time means more redo logs are generated in the log area. When sizing the log volume, you need to consider following points:
The redo logs must not be overwritten before a savepoint entry is available in data volume. This might cause SAP HANA system unable to restart. During the migration process, a very high workload needs to be processed, so it would be better to allocate extra disk space for the log volume in case of regular redo log backups fail for some reason during the migration.
The result of memory sizing usually determines sizing of the log area. If the total memory requirement is less than 512GB, log area should be at least half of the total memory requirement. If your system requires more than 512GB memory, you should at least allocate 512GB (preferably a little more) for the log area.
For single-node SAP HANA installations, the recommended disk size requirements for /hana/shared/<SID> is same as the total memory required:
For scale-out SAP HANA installations, the recommended disk size requirements for /hana/shared/<SID> depends on the number of worker nodes. Per each worker node of a scale-out system, a disk space of 1xRAM per 4 worked nodes required.
For example;
3+1 system, 512GB per node, total disk size = 1x512GB = 512GB
4+1 system, 512GB per node, total disk size = 1x512GB = 512GB
5+1 system, 512GB per node, total disk size = 2x512GB = 1TB
The size required for backup directory depends on your backup policy and backup frequency, but it must be larger than total size of data and log area.
CPU sizing
CPU requirements for migrating to SAP HANA standalone system are difficult to anticipate as we have no real references against which to compare. Therefore, the sizing refers to the following formula:
- 300 SAPS per active user by 65% for a CPU utilization buffer
Ring Sizing Tool For Sale Tool
An active user that consumes CPU at a given point of time. In sizing, it is usually overestimated the overlapping activity patterns of the end users. Some end users may also perform more or less intensive calculations on DB level. Consider this recommendation as an initial estimation that needs verification, the more users on the system the less likely the above formula would be accurate. SAP HANA servers with two sockets, for example, can deliver around 60000 SAPS. If you want to verify the CPU requirements, a test with the top 10 SAP HANA transactions could be really helpful either with a single user test or load test.
Now you should be able to describe the sizing of memory, persistence and CPU and what needs to be taken into consideration for sizing an SAP HANA server. Go ahead and run the SAP Quick Sizer, give it a try 🙂
Have any questions about sizing SAP HANA? Leave a comment below.
References and further reading:
SAP Note 1514966 – SAP HANA 1.0: Sizing SAP In-Memory Database
SAP Note 1793345 – Sizing for SAP Suite on HANA
SAP Note 1872170 – Business Suite on HANA and S/4HANA sizing report
SAP Note 1637145 – SAP BW on HANA: Sizing SAP In-Memory Database
SAP Note 1736976 – Sizing Report for BW on HANA
SAP Note 2055470 – HANA on POWER Planning and Installation Specifics – Central Note

Stair Case Sizing Tool For Laminate Floor
SAP Note 2188482 – SAP HANA on IBM Power Systems: Allowed Hardware
Sizing Tool For Ring
If you liked this post, you might like these relevant posts:
Feel free to share.